Best practices, Deliverability
Best practices, Deliverability

Do you know why some of your emails end up in the spam folder while others fail to reach recipients altogether? The answers lie in two critical concepts in email marketing: delivery rate and deliverability. While they sound similar, their meanings and impact on campaign effectiveness differ significantly.
Imagine sending a letter. The delivery rate tells you whether the letter made it to the recipient’s post office. However, it doesn’t confirm whether it ended up in their mailbox. Deliverability, on the other hand, answers whether the email landed in the primary inbox rather than in spam or other tabs.
In email marketing, simply arriving on the recipient’s server isn’t enough – it’s vital to consider where the email appears. This article explores the differences between these two metrics, how they affect your campaigns, and what you can do to ensure your messages land in the right place: the recipient’s inbox instead of disappearing into digital oblivion.
The delivery rate is a fundamental metric in email marketing, showing whether your sent emails reached recipients’ servers. It’s expressed as the percentage of emails that weren’t bounced compared to the total number of sent emails.
The formula for delivery rate is straightforward:
For example: If you send 1,000 emails and 20 bounce back, your delivery rate is:
[(1,000 – 20) ÷ 1,000] × 100% = 98%
This metric tells you whether your messages reached the recipient’s server, but it doesn’t reveal where they landed – in the primary inbox, spam folder, or elsewhere.
Emails may fail to reach recipients for two primary reasons: hard bounces and soft bounces.
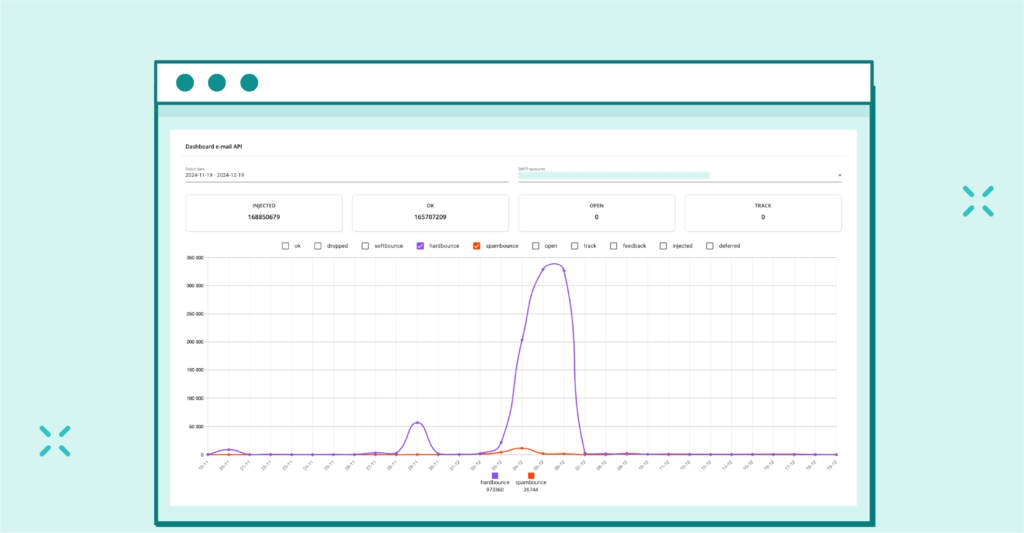
In the EmailLabs panel you can monitor information about email statuses and bounce types.
Email Delivery Failure: Common Causes and How to Fix It
Deliverability goes beyond confirming an email reached the recipient’s server. It is a key performance indicator that shows where your email ultimately ends up – whether in the primary inbox or perhaps in one of the tabs like Promotions or Notifications. Deliverability determines whether your email will be noticed and opened.
One of the most important metrics in email marketing is Inbox Placement Rate (IPR). It indicates how many of the sent emails were delivered to the recipient’s primary inbox. While significant, it is essential to remember that messages can also land in other tabs, which still impacts their effectiveness.
The delivery rate measures how many emails reached the recipients’ servers but does not provide a complete picture of their effectiveness. In contrast, IPR reveals whether the emails landed where they have the highest chance of being opened – in the primary inbox.
To better understand how IPR works, let’s use a simple example:
If 1,000 emails were sent, 900 were delivered (with no bounces), and 800 of them landed in the primary inbox, the IPR would be:
800 / 900 × 100% = 88.9%
Calculating IPR might seem straightforward, but in practice, it is far more complex. The formula above applies to an ideal situation where precise data is available about the number of delivered emails and those that landed in the primary inbox. In reality, obtaining such data is challenging, and accurate IPR calculations require advanced tools and are often based on estimations.
Email service providers (ESPs), such as EmailLabs, cannot measure IPR because they lack the technical ability to determine which tab the emails sent via their servers have landed in.
Why is that?
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
Ensuring your emails reach the intended inbox is a critical aspect of email deliverability, and monitoring the Inbox Placement Rate (IPR) plays a vital role in this process. The IPR measures the percentage of emails that land in recipients’ primary inboxes versus spam or other folders. Accurate monitoring of IPR provides insights into the effectiveness of your email campaigns and helps identify potential issues with deliverability.
To estimate the IPR, specialized deliverability testing tools, such as email seed lists, are commonly used. A seed list is a group of test email accounts created across a variety of email service providers (ESPs) like Gmail, Yahoo, and Outlook. These test accounts mimic your recipients’ email environments, enabling you to gauge where your emails are being delivered. By analyzing the data from seed list testing, you can identify whether your emails are reaching the inbox, spam folder, or being blocked altogether.
Deliverability is the final and most crucial stage of your email’s journey. It’s not just about hitting the “send” button but ensuring your message reaches the intended recipient in their primary inbox – where it is most likely to be noticed and acted upon.
Without strong deliverability, even the most well-crafted email campaigns can fall short, resulting in lost opportunities and wasted effort. But why exactly is deliverability so important? Let’s break it down.
In summary, email deliverability matters because it ensures your message gets seen, fosters stronger connections with your audience and drives tangible results for your business. Prioritizing deliverability is not just a technical necessity but a strategic advantage that can make or break your email marketing success.
Although the delivery rate and deliverability are often used interchangeably, they refer to two different stages of the email-sending process. Both are crucial to the success of a campaign but serve distinct roles. Let’s explore the key differences:
| Feature | Delivery Rate | Deliverability |
|---|---|---|
| What it measures | Whether the email reached the server. | Where the email landed after delivery. |
| Common problems | Technical errors (e.g., invalid emails). | Emails going to spam folders. |
The delivery rate indicates whether emails reached recipients’ servers – a basic requirement for an effective campaign. A low delivery rate signals issues with mailing lists, server configuration, or technical errors.
Example:
Even with a high delivery rate, deliverability determines whether emails land in the primary inbox or elsewhere. High deliverability ensures visibility, while low deliverability reduces the likelihood of engagement.
Example:
Effective email marketing is not just about crafting beautiful messages; it’s primarily about ensuring they reach the recipients. A high delivery rate and deliverability are critical metrics that significantly impact the success of your campaigns. Below are practical tips to help you achieve better results.
Do you want your emails to land directly in recipients’ inboxes and deliver the desired results? You need to understand that delivery rate and deliverability are two interconnected but distinct concepts.
Effective email marketing is the art of balancing both. For your campaigns to achieve their business goals, you must ensure not only that your messages reach recipients’ servers but also that they end up where they should – in the right inbox tabs where they can engage your audience.
Want to learn more? Check out other valuable articles on the EmailLabs blog and explore proven methods to optimize your email marketing campaigns.
We live in a world where your customers switch seamlessly between laptops, smartphones, and tablets. They navigate a complex digital ecosystem – checking emails, using mobile apps, and reacting...
We are delighted to announce that Vercom S.A., the company behind the EmailLabs project, has successfully completed the ISO 22301 certification process. This significant achievement underscores our commitment to...
EmailLabs, as part of the Vercom group, proudly announces its full commitment to aligning its ICT services with the latest cybersecurity standards. In response to dynamically changing regulations, the...
We are pleased to announce that MessageFlow, a product from the Vercom S.A. group, has received the prestigious CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) Certification. This recognition not only underscores the...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
When an email travels from sender to recipient, it passes through several critical components of email infrastructure. At the heart of this journey sits the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)...
Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi
The world of email marketing is constantly evolving, and leading mail service providers – Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and Apple – regularly update their guidelines for senders. In recent years,...
Gmail, Google and Yahoo's Requirements
You might have noticed a new item in your Gmail sidebar recently – the “Manage subscriptions” tab, often flagged with a blue notification dot. While Google announced this feature...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
Efficient email communication isn’t just about sending messages — it also involves integrating email functionality into your business systems and applications. Email APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) serve as the...
One of the most important yet often underestimated elements in shaping a company’s brand perception is the transactional email. In e-commerce, the design of such messages must be carefully...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Yahoogle
2024 brought fundamental changes to email marketing, introducing new, stringent requirements for senders. Since February 1, 2024, Google and Yahoo have started enforcing new deliverability rules, primarily targeting bulk...