The increasing number of phishing attacks each year, and the projection that this trend will continue to escalate, aren’t likely to astonish anyone. This can be attributed, in part, to the reality that these days, a significant portion of our business transactions occur online, like shopping through the Internet.
Consequently, this leads to a situation where a substantial amount of our personal data and details about our private lives or payment information such as credit card details are stored on various online platforms. While navigating the darknet, we might stumble upon numerous places where photos of our identification cards or other documents found in our mailboxes are up for sale or even being distributed for free.
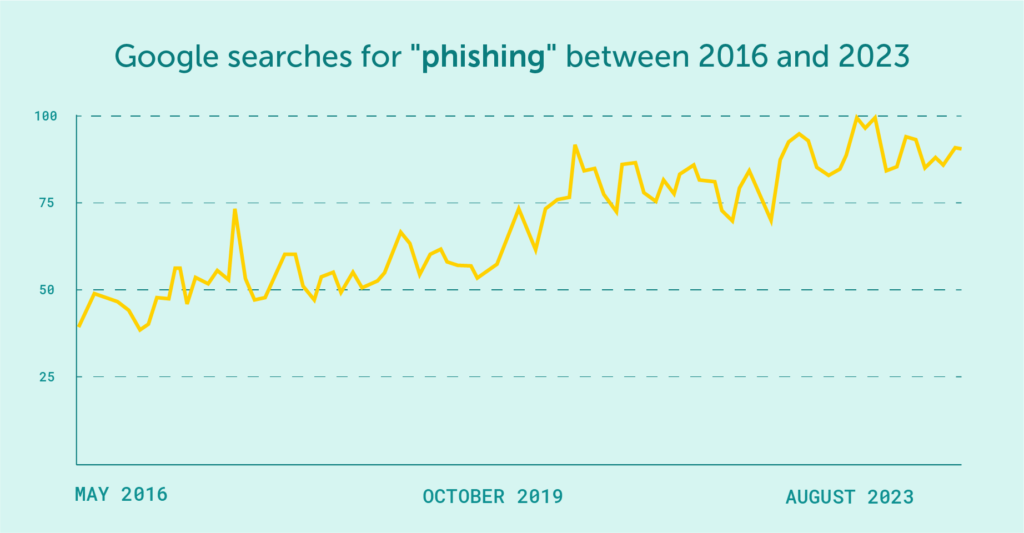
Source: Google Trends
It’s not surprising that cybercriminals, adopting the identities of trustworthy potential business partners, for instance, inundate us with messages attempting to deceive us into revealing our online accounts access information or infecting our computers and phones with malware.
While larger corporations are able to invest in more advanced security systems or teams like SOC (Security Operations Center) responsible for monitoring and analyzing an organization’s security, smaller businesses or startups can’t bear such expenses.
Partly due to this reason, this article was composed—to provide an introduction to the fundamentals and techniques that enable anyone to conduct a basic analysis of messages and attachments to identify potential malicious intent. This knowledge can shield more than one organization from unauthorized breaches of their systems.
Note: Accidentally running malicious files during analysis can lead to grave consequences. Nonetheless, the forthcoming advice is designed to mitigate the risk of infection as much as possible.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
In one of the primary articles within the CyberLabs series, I delved into the specifics of phishing attacks—a deceitful tactic involving the impersonation of trusted institutions, authorities, or individuals (like a bank, courier company, or public figure) to manipulate victims into performing actions that benefit the attacker, such as divulging login credentials.
CyberLabs #1 – Phishing being one of the most popular cyber threats
The phishing email itself, using social engineering or hacking people’s minds, may try to arouse fear in us, for example, and all in order to make us download and run malicious attachment which is hidden, e.g. under the form of an “invoice”.
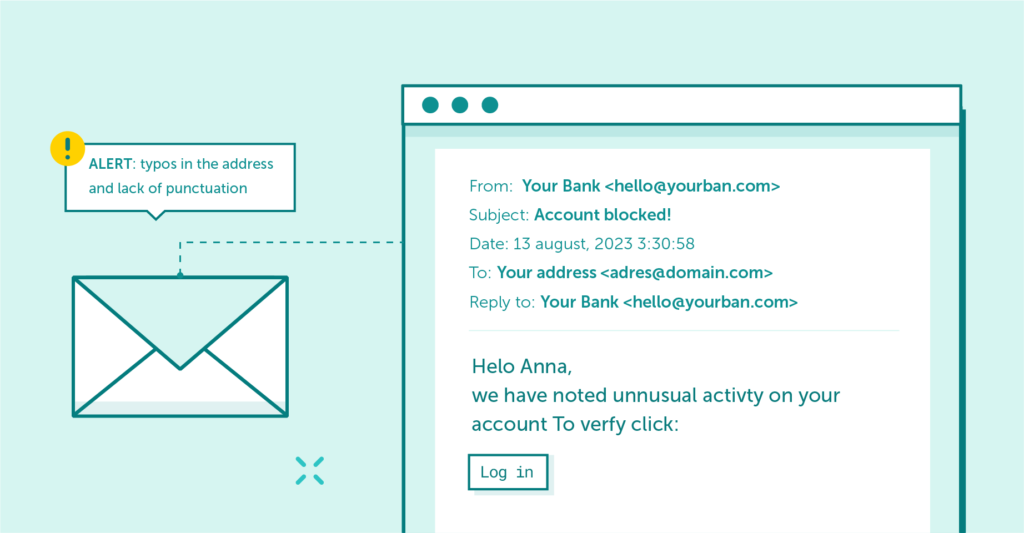
The phishing message above seemingly looks correct. However, it has spelling errors, no punctuation marks used, and was sent from an incorrect e-mail address.
Several forms of phishing attacks exist (I encourage you to refer back to the aforementioned phishing article), such as smishing or phishing via SMS, and vishing, where the perpetrator contacts the victim by phone, attempting to extract data like passwords, phone numbers, or general login information.
On the subject of vishing, it’s worth noting that recent weeks have seen numerous articles about ChatGPT or general AI, which have demonstrated the capability to mimic any conversational partner based on a voice sample (thus, envision a scenario where someone mimics our boss’s phone number and even sounds exactly like them).
Upon reflection, it becomes clear that with the assistance of artificial intelligence, the cyber-attacks directed at us could enter an even more hazardous realm, making the evasion of phishing attempts a more intricate task.
Undoubtedly, many of us view OpenAI’s ChatGPT as a groundbreaking solution capable of revolutionizing various markets. ChatGPT itself comes with inherent “safeguards” preventing the AI from generating responses that involve immoral or unethical actions, such as seeking personal or financial information.
Speaking of ChatGPT, it’s important to note that, similar to any system, this one also possesses certain “vulnerabilities.” It isn’t entirely devoid of weaknesses that could potentially be exploited by cybercriminals. These vulnerabilities provide openings through which we can craft text messages in a manner that prompts the artificial intelligence to respond to various questions or requests, even those of a less ethical nature (these vulnerabilities are continuously being addressed, but often as one loophole is closed, new methods emerge to sidestep the aforementioned restrictions).
Consequently, we’re able to task ChatGPT with tasks like retrieving passwords for legitimate email accounts from hashes. Moreover, we can request it to generate ransomware code (admittedly, the quality of the generated code might not be top-notch, but the mere possibility of generating such code should spark contemplation regarding its potential evolution in the upcoming years). It’s even plausible to use ChatGPT to compose phishing messages designed to extract personal, sensitive information from victims.
In contrast to many mass-sent phishing messages fraught with language errors and peculiar sentence structures that inherently arouse suspicion, these text-based communications exhibit a fluency that doesn’t immediately raise red flags.
Below, you can observe an example of such a message:
Certainly, the text message itself doesn’t encompass everything required to prepare for phishing scams. Nonetheless, currently, we often rely on the text and its sentence structure to gauge whether a message is dubious or not.
I’ve got some positive news for you! You’re on the verge of acquiring fresh techniques that can shield you from a multitude of phishing attacks.
Message headers, also known as email headers, constitute a segment of messages brimming with details about the email’s origins. This includes the genuine sender’s address, the recipient’s address, and security information like SPF/DKIM/DMARC specifications. Furthermore, you’ll come across fields like “Return-Path” / “Reply-To,” or “X-Spam Status,” which prove valuable in discerning whether an email is questionable and if it truly originates from the expected sender.
However, before we delve into the analysis of these headers, it’s crucial to know their location. This can vary quite a bit depending on the email client being used. Typically, the process involves opening the particular message, selecting “More,” and then opting for the “Show source / Show original” feature.
An exemplar set of headers might resemble the following:
Absolutely, you don’t need to undertake the following steps for every single email. Nevertheless, you can adhere to the provided instructions if you happen to receive an email that strikes you as suspicious for any reason. For instance, this might include an email containing an unfamiliar password reset link that you weren’t anticipating or one that makes an appeal for your credit card information.
Once you’re aware of where to locate message headers, you can embark on deciphering them. Acquiring knowledge about the significance of each header will certainly prove beneficial. Therefore, I’ve prepared a concise guide to these headers:
The headers y’all see up yonder are just a piece of the headers we might come across when we are sifting through a message. It’s good to bear in mind, too, that some mailboxes have their own headers what aren’t gonna show up in other places.
Peepin’ at them headers in their “raw” shape can be a mite overpowerin’ for some folks, so it’s handy to know ’bout tools that can help y’all analyze their headers. A few tools like:
For the tools I mentioned, all y’all gotta do is copy all the headers from that message, and the tool’s gonna give y’all back a report what’s easy on the eyes.
As we could read in the earlier part of the article, the Received header indicates to us the server from which the message was sent. Using this knowledge with the Cisco Thalos tool, we can check the reputation of the server from which the questionable emails were sent.
All we must do is place the IP address or domain address of the server responsible for sending the message onto the specified webpage. Through the response, we will gain insights into the server’s reputation, including whether it has been flagged as suspicious or has a history of sending spam, for instance. Furthermore, we will acquire details regarding the volume of messages dispatched and information related to the domain itself.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
Simply scrutinizing the email header might not suffice to ascertain the legitimacy of the text message we’ve received. There’s a possibility that cybercriminals have taken precautions and are utilizing a meticulously crafted infrastructure that doesn’t appear on any blacklists and isn’t marked as malicious.
The content of the message itself can instill confidence in us, as it may be skillfully composed with impeccable grammar and sentence structure. If the wrongdoer dedicates themselves to the task, the message can closely mimic the original, creating a convincing illusion. Typically, such messages contain either an attached file (we’ll delve into malicious files later) or a link. This link may either redirect us to a page requesting our credentials or lead us to an external phishing website offering downloads that might harbor malicious software.
Hence, our next step in thwarting phishing attempts involves verifying the trustworthiness of these links. Criminals frequently refine their tactics, so it’s essential to be aware of their methods.
A widely employed phishing technique by criminals involves leveraging reputable websites to host malicious files. It’s the links leading to these phishing or malware-infested sites that can thwart a successful attack. Suspicion may arise if the URL comprises a string of random alphanumeric characters.

We can consider links suspicious if they have random alphanumeric characters.
Hence, it’s crucial to note that cybercriminals frequently exploit well-known domains that we all recognize, such as Google Drive, Dropbox, Slack-Files, Discord, and various others, to either embed malware or establish phishing sites. You can access the comprehensive list of domains utilized for such purposes on this website.
Clicking on links leading to counterfeit websites or downloading malicious files can result in severe repercussions. Therefore, I strongly discourage anyone who is uncertain about their actions from engaging in such activities. Nevertheless, based on the link we possess (which we can easily copy), we can perform some rudimentary text message analysis. Below, you’ll find a few tools that can prove valuable for this purpose:
Certainly, there are indeed numerous similar sites available, but for fundamental analysis, these tools should certainly suffice. In the upcoming section of the article, I will provide a brief introduction to file analysis tools, which can also be employed in conjunction with link analysis.
There are instances where we won’t come across any links in an email. Instead, all we’ll find is an attachment, such as a purported invoice. Even if the message appears legitimate and the entire attack seems well-crafted, we should exercise caution before downloading and opening such attachments. It’s essential to maintain a sense of skepticism and remain vigilant.
Over the years, the nature of malicious files and phishing attacks has evolved. We may have heard of attacks that utilize Office files containing malicious macros. However, Microsoft eventually took steps to disable macros by default. As a result, criminals shifted their tactics to sending files associated with OneNote. These files may adopt various disguises, such as appearing to be invoices, and may contain buttons that, once clicked, trigger malicious actions.
One might also come across attempts to send files with a double extension, such as “invoice.pdf.exe,” where the fake “.pdf” extension is just a part of the file name. Another common method involves sending file archives, like .zip or .iso, often with password protection, concealing malicious content within. It’s worth noting that there are myriad techniques criminals employ to hide malware and distribute it through phishing emails.
In this segment of the article, I’d like to introduce additional software programs that can help us determine whether a file is malicious. However, it’s crucial to emphasize that our first line of defense should always be our antivirus software, which should be capable of handling most “mass” attacks. So, remember to keep your antivirus software active and regularly updated..
If the antivirus itself fails to detect anything, we can also employ the following online tools:
In addition to the aforementioned tools, it’s worth emphasizing the importance of Virustotal, as mentioned earlier.
As we conclude this section, it’s crucial to recognize that the activities outlined here are fundamental and should not be considered a replacement for the advanced analysis performed by specialized security teams. Nonetheless, I trust that the methods of analysis presented here will contribute, even if in a modest manner, to enhancing your overall security.
Certainly, you can report any messages that appear suspicious or lead to malicious websites. If you’re a Gmail user, you can do this directly from your inbox. When you open a suspicious message, simply click on “more options” and then choose either “Report Spam” or “Report phishing attempt.”
However, if you use a different ISP, don’t worry; there are still options available to you for reporting such attempts. Several websites and organizations allow you to report suspicious messages and phishing attempts. Some of these include:
Reporting such incidents can indeed be a significant contribution to cybersecurity. It’s crucial to understand that hackers can target anyone, not just large companies. Cybercriminals may have an interest in obtaining your personal and financial information, and failing to take proper security measures can lead to unpleasant situations.
Therefore, it’s essential to prioritize your online security and take steps to protect yourself from potential threats. Your vigilance and proactive actions can go a long way in safeguarding your digital presence and contributing to a safer online environment for everyone.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
A General Rule How to Prevent Phishing Attacks
By following these tips and maintaining a vigilant mindset, you can significantly reduce your vulnerability to phishing attacks and contribute to a safer online environment.
Stay Secure 👾
Gmail has announced significant changes in the requirements for email senders to maintain a good reputation and proper classification of messages in user inboxes starting from February 1, 2024....
Vercom S.A. public joint-stock company to which the EmailLabs project belongs, has been assessed and certified to be compliant with the ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27018 standards. The Vercoms’...
The increasing number of phishing attacks each year, and the projection that this trend will continue to escalate, aren’t likely to astonish anyone. This can be attributed, in part,...
Out of all the things that can go wrong when sending out marketing emails, having your emails end up in the recipient’s spam folder is arguably the most dreaded...
Email Authentication, Security
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that is designed to give domain owners the ability to protect their domain from unauthorized use, commonly known as email spoofing. Spoofing occurs...
With the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic, many brands have been challenged to adapt in a short period to the changed reality and new consumer attitudes. That meant reorganizing...
Have you ever sent an email in haste and immediately wished you hadn’t? It happens more often than we’d like to admit. If you ever find yourself in this...
One safe and easy way to keep track of your digital interactions is to save emails as PDFs. However, do you know the best ways to easily turn your emails into PDF files? In this article, we’ll look into the different ways you can do to turn your emails into accessible PDF files. Let’s start! Key Takeaways To save emails...
Sending large files online can sometimes feel like maneuvering through a maze with unexpected twists and turns. The frustration of hitting attachment size limits or dealing with slow uploads...
Have you ever sent an email in haste and immediately wished you hadn’t? It happens more often than we’d like to admit. If you ever find yourself in this...
One safe and easy way to keep track of your digital interactions is to save emails as PDFs. However, do you know the best ways to easily turn your emails into PDF files? In this article, we’ll look into the different ways you can do to turn your emails into accessible PDF files. Let’s start! Key Takeaways To save emails...
Sending large files online can sometimes feel like maneuvering through a maze with unexpected twists and turns. The frustration of hitting attachment size limits or dealing with slow uploads...
Are you a bit baffled by email protocols like IMAP, POP3, and SMTP? Have no fear – this article is here to explain it all. If you have ever...
In 2024, global providers like Gmail and Yahoo have implemented a series of changes, primarily targeting bulk senders. These changes, already in effect, are part of a continuous update...
In the face of dynamic technological advancements and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, ensuring network security has become crucial. Dozen security incidents present a challenge that we cannot afford to...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements
2024 marks a turning point in the fast-paced world of email deliverability, as this is the year when Google and Yahoo updated their sender requirements. With the enforcement period...
Best practices, Email Marketing
B2B email marketing – it’s a term you’ve likely heard before, but what does it really entail? And, more importantly, how can it be done effectively? In this article,...
Deliverability, Sending Reputation
Email sender reputation is one of the most important factors that can determine whether your emails reach the intended recipient or not. So, what is the email sender reputation,...