
The Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) holds significant importance in the realm of email communication. As a vital component of mail servers, SMTP takes charge of sending, receiving, and relaying email messages, ensuring that emails are delivered promptly and efficiently to their intended recipients.
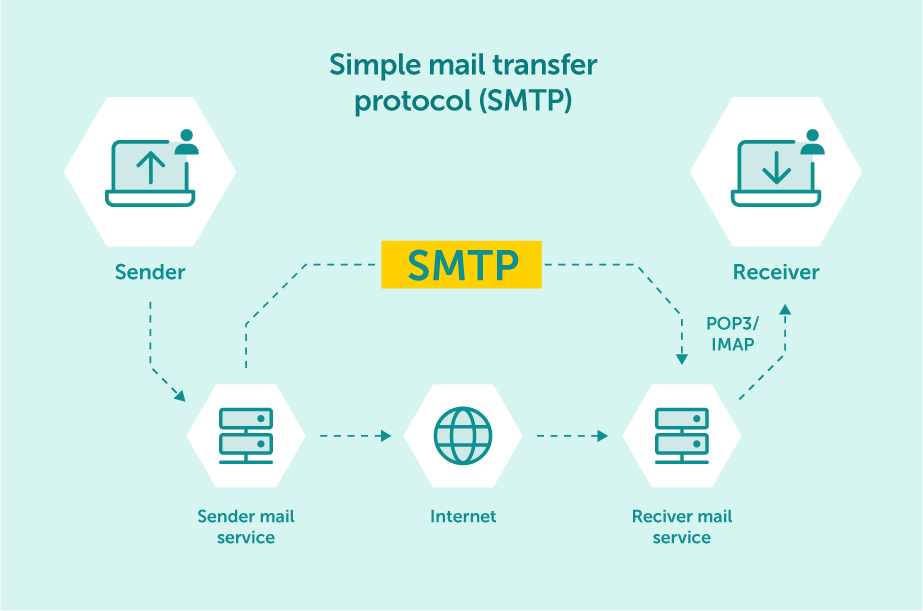
When an email is sent, it’s transferred over the internet from one server to another using SMTP.
When discussing SMTP ports, we often come across two particular numbers: Port 465 and Port 587. What differentiates these two seemingly similar entities?
To answer this question, we must dive into their contrasting features and examine the unique functions each port serves. Armed with this knowledge, you will be able to make informed decisions regarding your email configurations and ensure optimum security and efficiency in your online communications.
Let’s get started.
An SMTP port, or Simple Mail Transfer Protocol port, is a communication endpoint that handles information transfers from one server to another. It ensures the correct email data is delivered to the intended destination.
In essence, SMTP ports facilitate smooth communication between servers. Without these ports, the seamless exchange of emails we’ve grown accustomed to would be impossible.
These ports provide a standardized method for email clients and servers to transmit messages across networks in a secure and reliable manner. This standardization simplifies the process and allows for interoperability between various email systems on the internet.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
To understand the importance of SMTP ports, think about them as mediators in conversations between mail servers.
When an email is sent, the sender’s mail server connects to the recipient’s mail server using a specific SMTP port. This connection allows both servers to communicate and exchange information about the message being transmitted.
Once the necessary information has been exchanged and verified, the recipient’s mail server accepts the message, delivering it to the intended inbox.
In other words, a “port” serves as a bridge to help computers, such as two mail servers, communicate effectively with one another.
To clarify this concept, consider the following analogy: an IP address represents the physical street address of an apartment block. At the same time, a port signifies the number of a specific apartment within that block.
When delivering something to a particular person, merely addressing it to the apartment block isn’t enough; you also need a way to guarantee it reaches the correct location inside the block.
This is where an SMTP port steps in, acting as a fast and secure connection method.
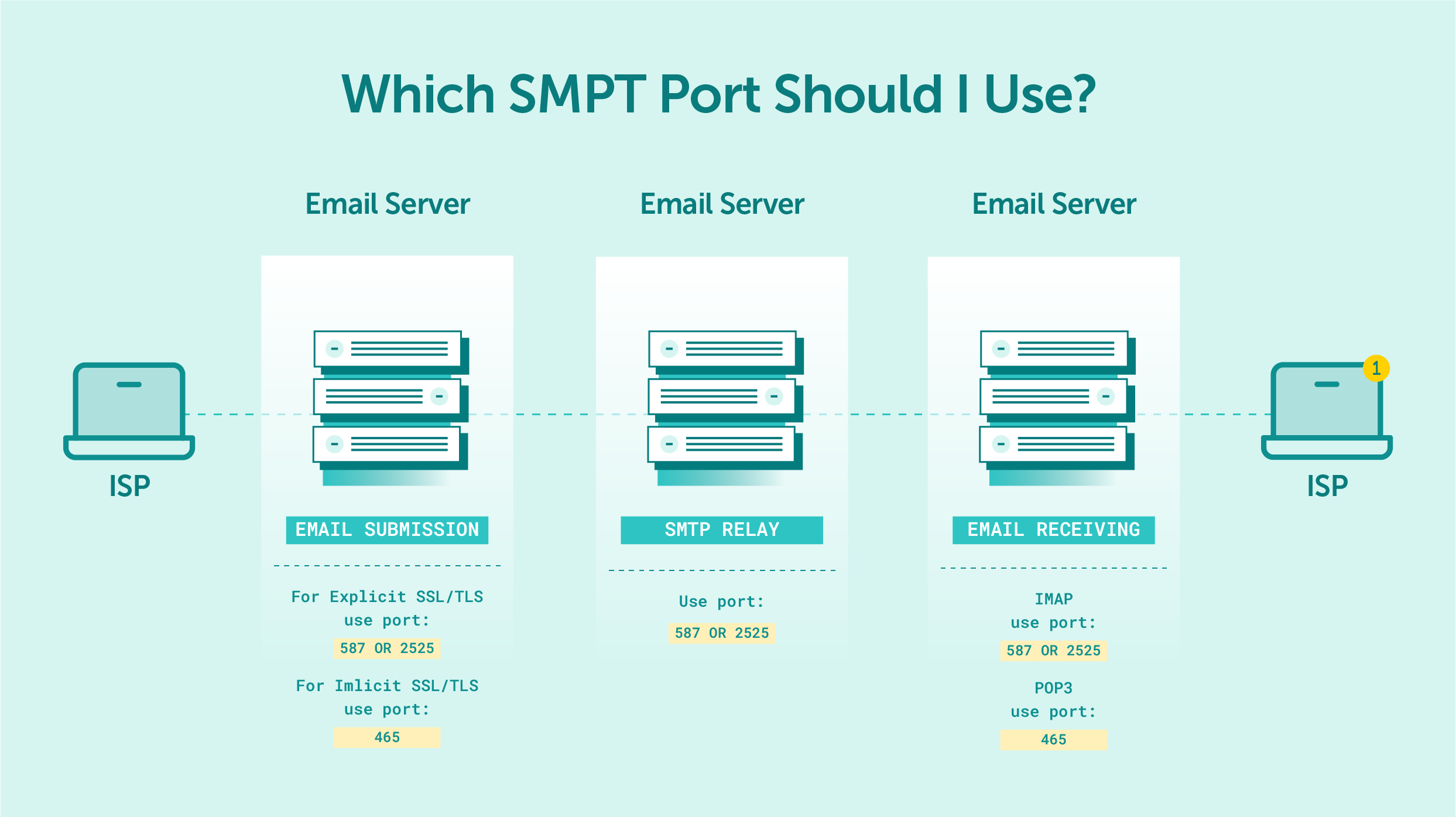
Receiving email is facilitated by the IMAP or POP protocols, each of which relies on different ports.
Before diving into the specifics of Port 465 and Port 587, it’s important to understand some historical context. The development of SMTP ports has been influenced by various factors over time, with security being a primary concern.
The oldest SMTP port is Port 25, which was initially designated as the default transmission channel for SMTP communications. This standard SMTP port was widely used for many years. Yet, as technology advanced and new challenges emerged, it became necessary to introduce new port numbers for more secure transmission.
Over time, issues with spam and compromised computers led to increased scrutiny of Port 25. Spammers often exploited this port to send unsolicited emails from infected machines, causing headaches for both users and internet service providers (ISPs).
In response, residential ISPs began blocking Port 25 to prevent spamming from compromised computers. This change marked a significant shift in the landscape of email communication and prompted the development of new protocol commands to secure email message transmissions.
The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) took the lead in addressing these challenges, working diligently on creating separate ports for email submission and message relay.
The IETF aimed to provide more secure connections and better control over the flow of incoming mail by establishing distinct ports for different functions. This move enhanced security and paved the way for the introduction of Ports 465 and 587, each serving unique purposes within the realm of email communication.
Two governing bodies oversee specific aspects of internet technologies and assignments: the Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) and the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). Both organizations play critical roles in ensuring the smooth functioning of the internet, but their responsibilities differ in certain areas.
Firstly, the Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) is accountable for three primary concerns of internet regulation: domain names, number resources, and protocol assignments. As part of its role, IANA maintains a comprehensive list of service protocols and ports, which is crucial for understanding various internet services and applications.
IANA stands for the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority. It is a global organization that oversees the allocation and assignment of various Internet-related parameters, such as IP addresses, domain names, and protocol port numbers.
Although anyone can register a new service as long as the port is available, it’s crucial to note that registration with IANA does not guarantee the traffic to or from this port is “good” or legitimate. Instead, IANA’s role is primarily focused on keeping track of these assignments and ensuring there is a central point of reference for available ports and protocols.
On the other hand, the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) is an organization dedicated to publishing standards aimed at improving the functionality and efficiency of the internet.
The IETF works through a collaborative approach by using Requests for Comments (RFCs) to propose new changes or enhancements to existing internet technologies. These RFCs are open for discussion and feedback from industry experts, researchers, and other interested parties before being accepted as official standards.
The IETF is responsible for creating and maintaining various Request for Comments (RFC) documents that define the standards and protocols used on the Internet.
Thanks to it, any proposed changes undergo thorough evaluation and testing before implementation, leading to a more robust and reliable internet infrastructure.
Ultimately, while IANA’s primary responsibility lies in managing domain names, number resources, and protocol assignments, the IETF focuses on developing and improving internet standards through a collaborative approach involving RFCs.
Together, these organizations play a critical role in maintaining the stability, security, and efficiency of the global internet ecosystem.
As mentioned above, Port 25 has long been the default port for SMTP transmission, serving as the standard channel for sending email messages since the inception of the internet.
As one of the most common SMTP ports, its original purpose was to facilitate SMTP relaying between mail servers. This allowed email messages to be sent from one server to another, serving as a message relay port for efficient communication.
Nonetheless, as the internet grew and security threats emerged, existing ports like Port 25 began to show their limitations. Cybercriminals exploited the lack of encryption on this default port, intercepting and tampering with email messages in transit.
Today, some mail servers still use Port 25 for SMTP relay, but it’s becoming increasingly rare due to its inherent security vulnerabilities.
As new technologies continue to advance and security risks become more sophisticated, we’ll likely see a gradual phase-out of Port 25 in favor of more secure SMTP transmission options.
Port 465, initially registered by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) as the “URL Rendezvous Directory” for SSM, quickly became a popular choice for encrypted connections. It sends emails using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). It’s now commonly known as the implicit TLS (Transport Layer Security) port.
When using implicit TLS on Port 465, an email client establishes a secure connection with the SMTP server immediately upon connecting. This method ensures that all data transmitted between the mail client and the server remains encrypted from start to finish. As a result, sensitive information is less likely to be intercepted or compromised during transmission.
However, despite widespread use and support from many mail servers, the IETF deprecated Port 465 in favor of Port 587. While some mail servers still prefer implicit TLS on Port 465, it’s no longer recognized as the default SMTP submission port by the IANA registry.
Recognizing the need for a more secure alternative to Port 25, the IETF introduced Port 587 as the default mail submission port. Unlike Port 465’s implicit TLS encryption, Port 587 uses a feature called STARTTLS to offer optional TLS encryption.
When an email client connects to an SMTP server via Port 587, it first initiates a plain-text connection. The client then sends an EHLO command to the server, which checks if the server supports TLS. If it does, the email client issues a STARTTLS command, and the server responds by encrypting all future communications during that session.
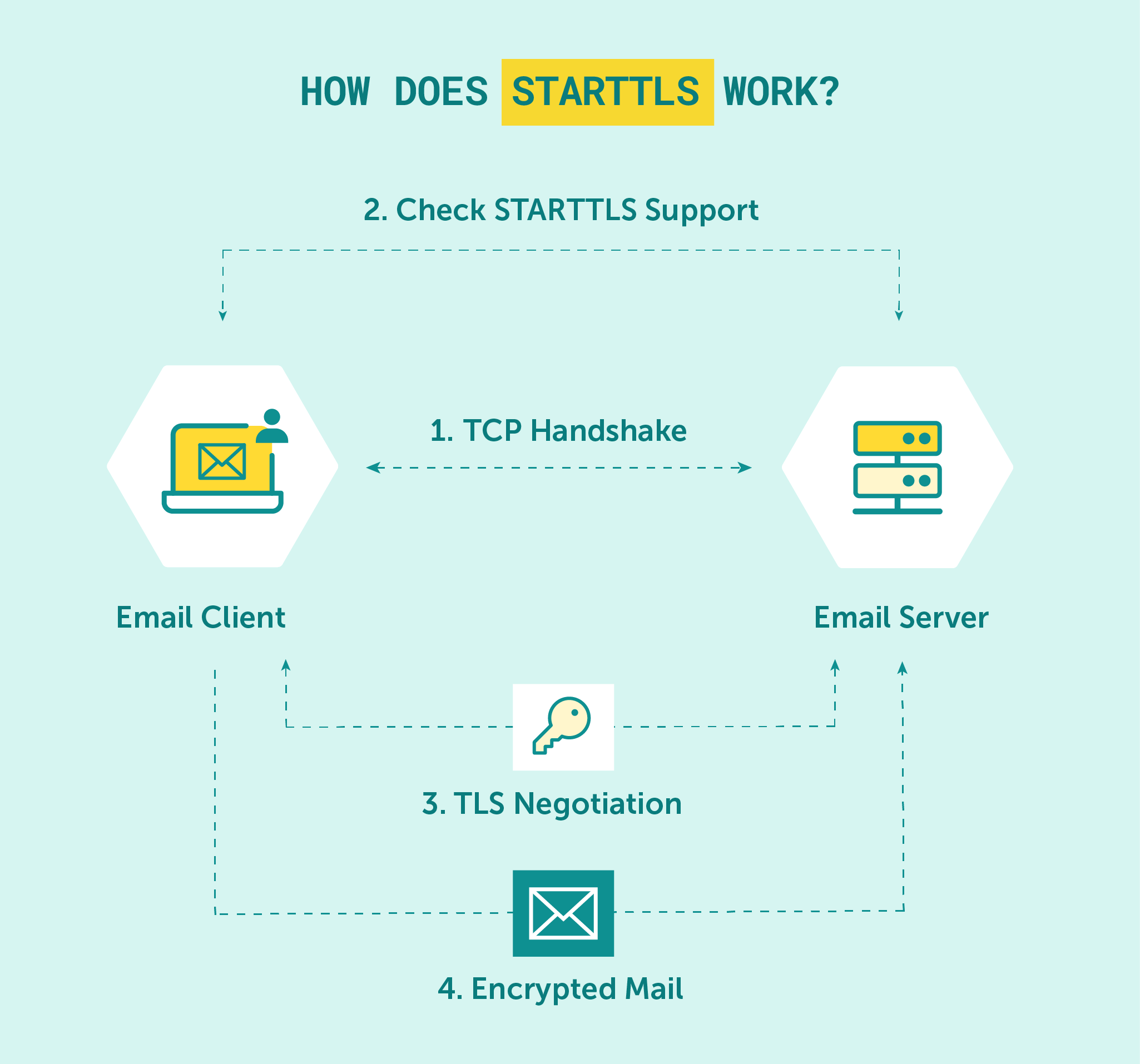
STARTTLS is a way to secure communications on-the-fly without requiring a separate port for encrypted connections.
This method allows for greater flexibility in terms of connection methods and is considered more secure than using the same port for both encrypted and unencrypted connections. Thus, port number 587 is widely regarded as the default SMTP port.
Port 2525 is another option that has gained popularity as an alternative message relay port. Although it’s not an officially recognized default port for SMTP transmission, many email service providers and cloud hosting solutions now support Port 2525 as a separate port for email message submission.
This port functions similarly to the more common SMTP ports, like 25 and 587, but it offers users an additional choice to bypass potential network restrictions or limitations.
Some ISPs may block existing ports like 25, making it challenging to establish a reliable connection between mail servers and clients. In such cases, Port 2525 can serve as a viable alternative, ensuring smooth and uninterrupted email communication.
Moreover, Port 2525 can be configured to use encryption methods like TLS to secure email messages during transmission. By encrypting communications, sensitive information contained within email messages remains protected from potential interception or compromise.
While both ports offer their advantages, choosing the proper mail server configuration that best suits your needs is essential.
In general, most email clients and SMTP servers now support and prefer Port 587 due to its flexible approach to TLS encryption and compatibility with modern security standards.
That being said, some older email clients may still default to using Port 465. In such cases, it’s crucial to consult your hosting provider or cloud hosting providers to ensure you’re using the correct port settings to maintain a secure and reliable connection between your email client and mail server.
By working with EmailLabs, your email client-to-email server communication will remain fast and secure. We can help you improve your deliverability, and increase your email reputation.
On top of that, using our services, you’ll maximize your sending speed, allowing you to reach your clients and associates lightning-fast.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
SMTP ports are an integral part of email communication, and throughout the years, the importance of particular ports and their relevance has only grown.
Ports 465 and 587 are two of the most commonly used ports for SMTP transmission, and both offer unique advantages when it comes to security and efficiency. Yet, with Port 587 now being the preferred option for modern email communication, it’s essential to understand what each port offers in order to make the right choice for your needs.
At EmailLabs, we understand how complicated this process can be. That’s why we provide services to help you improve deliverability, and maximize your email reputation.
Contact us if you have any doubts or concerns. We’ll be thrilled to help you!
We live in a world where your customers switch seamlessly between laptops, smartphones, and tablets. They navigate a complex digital ecosystem – checking emails, using mobile apps, and reacting...
We are delighted to announce that Vercom S.A., the company behind the EmailLabs project, has successfully completed the ISO 22301 certification process. This significant achievement underscores our commitment to...
EmailLabs, as part of the Vercom group, proudly announces its full commitment to aligning its ICT services with the latest cybersecurity standards. In response to dynamically changing regulations, the...
We are pleased to announce that MessageFlow, a product from the Vercom S.A. group, has received the prestigious CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) Certification. This recognition not only underscores the...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
When an email travels from sender to recipient, it passes through several critical components of email infrastructure. At the heart of this journey sits the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)...
Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi
The world of email marketing is constantly evolving, and leading mail service providers – Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and Apple – regularly update their guidelines for senders. In recent years,...
Gmail, Google and Yahoo's Requirements
You might have noticed a new item in your Gmail sidebar recently – the “Manage subscriptions” tab, often flagged with a blue notification dot. While Google announced this feature...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
Efficient email communication isn’t just about sending messages — it also involves integrating email functionality into your business systems and applications. Email APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) serve as the...
One of the most important yet often underestimated elements in shaping a company’s brand perception is the transactional email. In e-commerce, the design of such messages must be carefully...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Yahoogle
2024 brought fundamental changes to email marketing, introducing new, stringent requirements for senders. Since February 1, 2024, Google and Yahoo have started enforcing new deliverability rules, primarily targeting bulk...