Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Technical
Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Technical
The explosive growth of email-based cyber threats has transformed how we approach digital communication security. In 2004, Yahoo! introduced DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) to combat increasingly sophisticated email spoofing attacks, and by 2011, it became an Internet Standard through RFC 6376.
Let’s take a closer look at what this fascinating solution is and how it works.
DomainKeys Identified Mail (DKIM) represents a sophisticated email authentication protocol that serves as a cryptographic defense mechanism against email spoofing and manipulation. Unlike basic authentication methods, DKIM provides the ability to digitally sign email messages using asymmetric cryptography.
During some attacks, cybercriminals study the target of their attack very carefully to lull the recipients’ alertness. They use appropriate language and add characteristic data/phrases.
In simple terms, the message hash is signed using the private key stored on the mail server and verified using a public key published in DNS records. Think of it like a unique, tamper-proof seal on a physical letter. The sender (email server) applies the seal using a special tool (the private key) that only they possess. Anyone receiving the letter can check a public registry (DNS) to see what the sender’s official seal looks like (the public key) and verify that the seal on the letter is authentic and hasn’t been broken (message integrity).
The fundamental strength of DKIM lies in its cryptographic implementation, which involves:
The DKIM signing process implements a multi-stage verification workflow that validates both message integrity and domain authenticity.
When an email server sends a message, it first generates a DKIM signature by calculating a hash of selected email headers and the message body, then encrypts this hash with the domain’s private key. This encrypted signature becomes part of the email headers, creating a verifiable link between the message content and the sending domain.
A typical DKIM signature header looks like this:
DKIM-Signature: v=1; a=rsa-sha256; d=example.com; s=news; c=relaxed/relaxed; q=dns/txt; t=1126524832; x=1149015927; h=from:to:subject:date:keywords:keywords; bh=MHIzKDU2Nzf3MDEyNzR1Njc5OTAyMjM0MUY3ODlqBLP=; b=hyjCnOfAKDdLZdKIc9G1q7LoDWlEniSbzc+yuU2zGrtruF00ldcF VoG4WTHNiYwG
Each DKIM signature consists of tag=value pairs that provide critical information for email authentication. These components work together to create a robust verification system that helps receiving mail servers validate the authenticity of incoming messages.
| Tag | Description | Authentication Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| v= | Version identifier (always 1) | Ensures protocol compatibility |
| a= | Algorithm (typically rsa-sha256) | Defines the cryptographic method used |
| d= | Sending domain | Links signature to the authorized domain |
| s= | Selector for DNS lookup | Locates correct public key in DNS |
| b= | Cryptographic signature | Contains encrypted hash for verification |
| bh= | Body hash | Ensures message content integrity |
| h= | Signed header fields | Specifies protected email components |
Optional tags enhance email security by providing temporal validation and modification tolerance controls. These values help with intelligent filtering decisions, as spammers typically don’t include proper timestamp information.
| Tag | Description | Security Significance |
|---|---|---|
| t= | Signature timestamp (Unix epoch) | Helps identify spam as malicious senders rarely set timestamps |
| x= | Signature expiration time | Invalidates older messages, must be greater than the timestamp |
| c= | Canonicalization algorithm | Controls tolerance for transit modifications like whitespace changes |
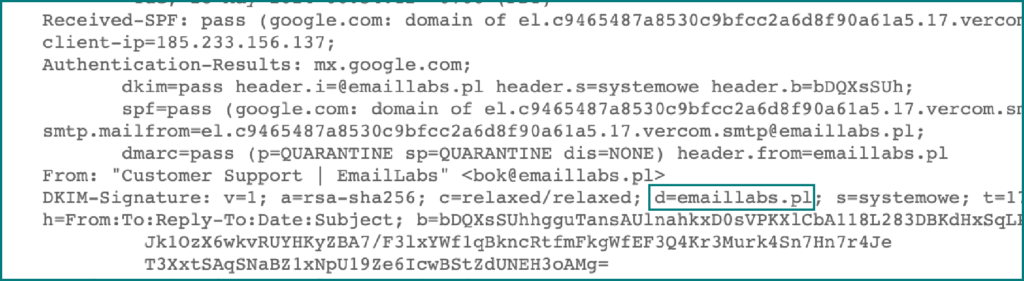
The DKIM Header is a type of authentication that involves adding a digital signature to the email.
While powerful, DKIM verification isn’t foolproof and can sometimes fail. Common causes include: incorrect configuration of the public key in DNS, issues with email forwarding services that modify signed headers or body content in transit, using expired private keys, or mismatches between the signing server configuration and the DNS record. Troubleshooting often involves carefully checking DNS settings and analyzing email headers for error codes.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
In 2024, major email providers Google and Yahoo introduced stringent email authentication requirements, a trend now joined by Microsoft effective May 5, 2025, making robust authentication crucial.
This fundamental shift mandates that bulk senders (those exceeding 5,000 emails daily to major consumer services like Gmail, Yahoo Mail, Outlook.com, Hotmail.com, etc.) implement valid SPF, DKIM, and DMARC configurations, including proper alignment and at least a `p=none` DMARC policy. Significantly, Microsoft begins actively rejecting non-compliant bulk emails starting May 5, 2025, reinforcing the industry-wide departure from optional authentication practices for high-volume senders.
The modern DKIM framework demands heightened security measures, with providers specifically requiring the implementation of the following critical elements:
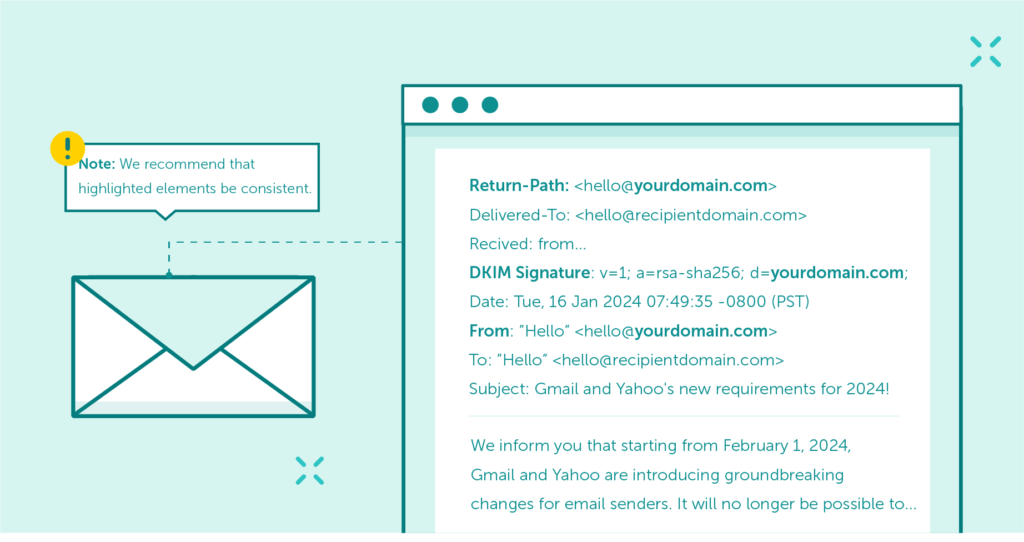
Domain alignment is a mechanism that ensures that the authenticated email domain is consistent with the domain found in the ‘From’ header address, representing the sender’s identity.
Together, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC form a layered framework for email authentication, with each protocol addressing different aspects of sender verification.
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) functions as a domain’s authorized server directory. It maintains a whitelist of IP addresses that can legitimately send emails from that domain. When an email server receives a message, it checks the sending server’s IP address against this SPF record to verify authorization.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) acts as the policy enforcer and decision maker, providing explicit instructions to receiving mail servers about how to handle messages that fail authentication checks.
While SPF focuses solely on validating the sending server’s identity through IP verification, DMARC provides a comprehensive policy layer that can leverage both SPF and DKIM results to make intelligent delivery decisions.
Using SPF and DMARC offers administrators granular control over how their domain’s emails should be treated when authentication checks fail.
EmailLabs provides a comprehensive email infrastructure solution that prioritizes secure email delivery through robust authentication implementations.
Our platform offers dedicated outbound servers for handling email dispatch from any application, e-commerce system, CMS, CRM, or marketing automation tool, with built-in support for essential authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
Through our advanced Email RESTful API and Cloud SMTP services, we help you ensure efficient email transmission and monitoring without any compromises in terms of security. Notably, EmailLabs simplifies DKIM setup through our Sender Authorization function, which automatically generates the necessary DNS records for you, ensuring proper configuration with minimal technical effort on your part.
The evolution of email authentication standards, particularly DKIM implementation requirements, reflects the growing sophistication of cyber threats and the email industry’s response to them.
As we progress through 2025, proper DKIM configuration has become not just a best practice but a fundamental requirement for maintaining email deliverability and protecting both senders and recipients.
Ready to secure your email infrastructure? Reach out and let us handle the complexities of email authentication while you focus on what matters most — reaching your audience with confidence.
We live in a world where your customers switch seamlessly between laptops, smartphones, and tablets. They navigate a complex digital ecosystem – checking emails, using mobile apps, and reacting...
We are delighted to announce that Vercom S.A., the company behind the EmailLabs project, has successfully completed the ISO 22301 certification process. This significant achievement underscores our commitment to...
EmailLabs, as part of the Vercom group, proudly announces its full commitment to aligning its ICT services with the latest cybersecurity standards. In response to dynamically changing regulations, the...
We are pleased to announce that MessageFlow, a product from the Vercom S.A. group, has received the prestigious CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) Certification. This recognition not only underscores the...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
Best practices, Maile marketingowe, Marketing E-mails, Transactional Emails
Mass email sending is a critical strategy for business owners, marketers, developers, and nonprofit managers looking to scale their outreach. Whether you are announcing a new product feature, distributing...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
When an email travels from sender to recipient, it passes through several critical components of email infrastructure. At the heart of this journey sits the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)...
Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi
The world of email marketing is constantly evolving, and leading mail service providers – Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and Apple – regularly update their guidelines for senders. In recent years,...
Gmail, Google and Yahoo's Requirements
You might have noticed a new item in your Gmail sidebar recently – the “Manage subscriptions” tab, often flagged with a blue notification dot. While Google announced this feature...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
Efficient email communication isn’t just about sending messages — it also involves integrating email functionality into your business systems and applications. Email APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) serve as the...
One of the most important yet often underestimated elements in shaping a company’s brand perception is the transactional email. In e-commerce, the design of such messages must be carefully...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Yahoogle
2024 brought fundamental changes to email marketing, introducing new, stringent requirements for senders. Since February 1, 2024, Google and Yahoo have started enforcing new deliverability rules, primarily targeting bulk...