Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi

The world of email marketing is constantly evolving, and leading mail service providers – Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and Apple – regularly update their guidelines for senders. In recent years, especially since early 2024, we have witnessed significant tightening of these requirements, particularly for bulk senders. The goal is not only better combat against spam and phishing, but also raising the overall quality of email communication and protecting users.
For companies and marketers, this means urgent adaptation of practices. The stakes are high: avoiding blocks and landing in spam folders directly impacts business results. This article serves as your comprehensive guide to the latest changes, helping you understand and implement the necessary steps to keep your email marketing campaigns effective.
If you wish to explore the specifics of requirements from individual players, please refer to our previous articles:
To better understand the context of current requirements, it’s worth looking at the timeline of their implementation:
It’s worth noting that major providers like Google or Yahoo did not implement these stricter rules overnight. They adopted a gradual rollout strategy, giving bulk senders time to adapt and minimizing disruption to legitimate email communication. Here’s how it played out for Google as an example:
Introduced “lenient enforcement” – a small percentage of non‑compliant bulk sender traffic (e.g., missing SPF/DKIM/DMARC, domain misalignments, missing unsubscribe headers) began receiving temporary SMTP errors (4xx, e.g., 450 4.7.26). These errors signaled problems but often allowed for automatic retry.
The share of traffic subject to restriction was gradually increased (gradual ramp-up). At the same time, permanent errors (5xx, e.g., 550 5.7.26) started to appear – meaning the message would be rejected without retry.
All emails from bulk senders not meeting requirements (including missing one‑click unsubscribe) became subject to outright rejection.
A similar (though often less transparent) approach was taken by Yahoo. Microsoft, when starting enforcement for consumer accounts in May 2025, also signaled clear consequences: messages would be rejected outright (REJECTED), not just spam‑flagged. In parallel, Gmail and Yahoo continued to steadily tighten their rules.
The evolution of sender requirements has brought about a change in how major providers assess sender quality. Here’s how two of the giants approach it differently.
A significant update in Google’s timing: despite earlier announcements about retiring the legacy (v1) Postmaster Tools at end of October 2025, Google decided to pause that process.
What does it mean for you?
Recommendation: Treat v1 as auxiliary. Base your deliverability decisions on v2 Compliance Status.
While Google focuses more on technical compliance, Yahoo – via its new “Insights” dashboard – emphasizes recipient experience. The key novelty is how Spam Complaint Rate (SCR) is calculated.
A comprehensive analysis of the new dashboard and all available metrics is available in our dedicated post: Yahoo Sender Hub “Insights”: Understanding the New Metrics.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
The domain visible in the “From” field (P2 Header From) must be aligned with the domain authenticated by SPF (the P1 domain – Return-Path/MailFrom) or the domain used in the DKIM signature (d=).
Alignment with DKIM is preferred and often more reliable. Providers — including Microsoft — emphasize this alignment to ensure that the visible sender is genuinely associated with the email authentication mechanisms.
It’s important to know that using subdomains for sending (e.g., newsletter.yourdomain.com) is fully acceptable and often recommended for better reputation management — as long as they are properly configured for SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
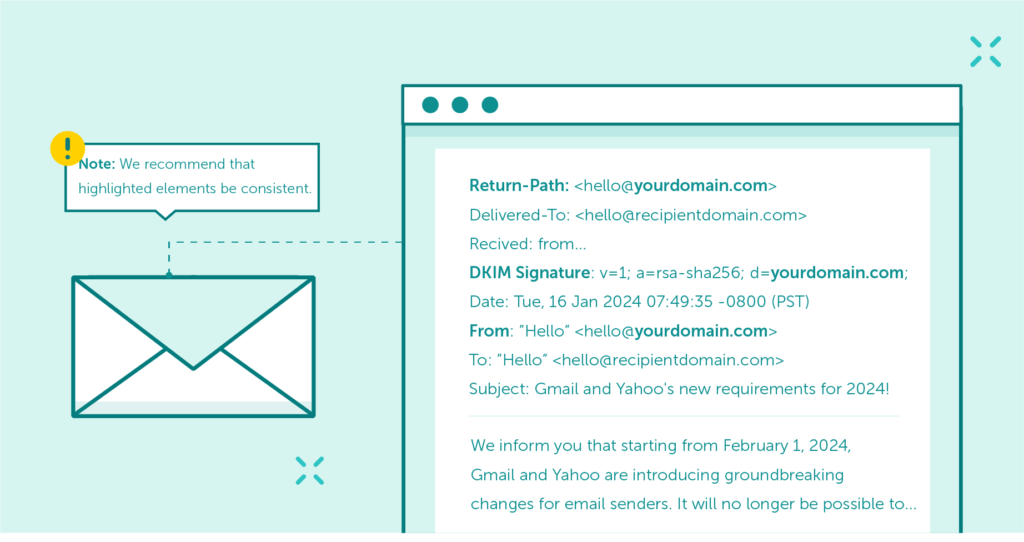
Domain alignment is a mechanism that ensures that the authenticated email domain is consistent with the domain found in the ‘From’ header address, representing the sender’s identity.
Promotional or subscription emails must include a clearly visible unsubscribe link (not hidden in fine print), and you must implement the proper headers: List-Unsubscribe (RFC 2369) and List-Unsubscribe-Post (RFC 8058). This ensures recipients can unsubscribe with a single click directly from their mail client (Gmail, Yahoo, Apple Mail, Outlook Web, etc.).
Unsubscribe requests must be honored promptly, usually within two days.
Keep the rate of complaints submitted by users below 0.3%, ideally under 0.1%. Exceeding these thresholds is a strong signal to providers that your messages are unwanted.
Actively monitor your spam complaint rate using Feedback Loop (FBL) reports made available by providers such as Google Postmaster Tools, Microsoft SNDS/JMRP, and Yahoo CFL.
Apple does not offer a traditional FBL service – instead, it emphasizes proactive list management and monitoring engagement metrics as a way to maintain a low complaint rate.
Sending IP addresses must have properly configured PTR (Reverse DNS) records that map the IP address to a domain name (hostname). This hostname should also have a corresponding A record (or AAAA record for IPv6). Correct DNS configuration is essential for improving email deliverability in marketing campaigns.
Consistency between forward DNS (A/AAAA) and reverse DNS (PTR) is crucial for building trust with receiving servers.
Email messages must be properly formatted in accordance with the standards defined in RFC 5322 (Internet Message Format) and related documents.
Compliance with these standards, i.e., correct email structure, is critical for proper interpretation by receiving servers.
Microsoft particularly emphasizes the importance of compliance in the “From” header (P2 Header From). This includes, among others, the following:
Ensure that the connection between your sending server and the recipient’s server is encrypted using TLS. This is standard, and expected by default, for modern email delivery.
If your messages are being forwarded (e.g., through mailing lists or forwarding systems), adding ARC headers (as defined in RFC 8617) helps preserve the results of SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentication at every stage of the forwarding process.
While it’s not always a direct requirement imposed on the original sender, supporting ARC is considered a best practice.
Use a consistent and easily recognizable name and “From” address when sending messages. This helps build trust with recipients and is positively evaluated by spam filters.
Although using addresses like “[email protected]” is not explicitly prohibited, providers such as Microsoft recommend that the “From” address (P2 From) is able to receive replies. This facilitates two-way communication and is perceived as more user-friendly.
Maintain the hygiene of your database and regularly review your mailing list, removing inactive addresses, addresses that generate hard bounces, and those who have requested to unsubscribe.
Process unsubscribe requests promptly, typically within two days, in accordance with the requirements.
Ignoring the new, unified mailbox provider requirements is not an option if effective communication matters to you.
The consequences of non-compliance can be serious and have a direct impact on your marketing efforts and sender reputation:
Your emails may be systematically rejected by receiving servers. This means that a significant portion of your communications won’t reach recipients at all.
Even if messages aren’t immediately rejected by Internet Service Providers (ISPs), there’s a high risk they’ll be automatically flagged as spam. This drastically lowers open and engagement rates.
Consistently sending emails that don’t meet standards leads to a decline in the reputation of your domain and IP addresses. Rebuilding trust with providers is a long and difficult process.
In extreme cases, especially when spam complaint rates remain high or fundamental mechanisms like unsubscribe options are missing, your sending domain or IP addresses may be fully blocked by major providers. This may also affect future emails, which will be more likely to end up in spam folders.
As part of the new enforcement phase, Gmail has introduced strict error codes for non-compliant messages.
If you don’t meet the requirements, you’ll see hard bounce errors in your logs, such as:
More information on how to prepare for enforcement and avoid blocks can be found in the article: Gmail Enforcement 2025 – Google Begins Blocking Non-Compliant Email Sends.
As of November 2025, Gmail has introduced much clearer bounce error messages for email senders.
Instead of generic codes, servers may now return precise explanations, such as:
For example, Microsoft has clearly communicated that as of May 5, 2025, it is rejecting non-compliant emails sent to consumer addresses (Outlook.com, Hotmail, Live.com).
What’s more, it has confirmed that, contrary to earlier indications, such messages are being immediately rejected (REJECTED) and not merely routed to the spam folder.
This means the messages will not reach the recipient in any form. Gmail and Yahoo are taking a similarly increasingly strict approach.
In short, non-compliance with the new standards is a direct path to significantly reduced effectiveness of your email marketing campaigns, and loss of contact with your audience.
| Requirement / Provider | Gmail | Yahoo | Microsoft (Outlook.com, Hotmail, Live.com) | Apple Mail |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition of Bulk Sender | >5,000 emails/day | Sending the same content to multiple recipients (general definition) | >5,000 emails/day to consumer addresses | No strict numerical threshold; emphasis on best practices for all senders |
| SPF | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| DKIM | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| DMARC | Required (min. p=none; p=quarantine/reject for BIMI) | Required (min. p=none) | Required (min. p=none; Microsoft strongly recommends p=quarantine or p=reject and suggests these may become standard in future updates) | Required (recommended p=quarantine or p=reject) |
| Domain Alignment | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| One-Click Unsubscribe | Required easy opt-out (link + List-Unsubscribe & List-Unsubscribe-Post headers) | Required easy opt-out (List-Unsubscribe & List-Unsubscribe-Post headers); unsubscribe link in message body also expected (practically treated as mandatory) | Required easy opt-out (link + headers) | Required easy opt-out (link + headers) |
| Spam Complaint Rate | <0.3% (ideally <0.1%) | <0.3% (ideally <0.1%) | No officially published threshold; maintaining a low rate is recommended best practice | No public FBL mechanism; focus on message quality and user engagement |
| PTR Record | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| RFC 5322 Formatting | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| TLS Encryption | Required | Required | Required | Required |
| Enforcement Timeline | Feb 2024: Temporary errors for non-compliant messages Apr 2024: Gradual rejection Jun 2024: Full enforcement |
Feb 2024: Start of enforcement Jun 2024: One-click unsubscribe requirement and full enforcement |
May 5, 2025: Start of full enforcement – non-compliant emails are rejected, not just flagged as spam | Requirements fully effective; enforcement began gradually after official guidelines were published on Feb 25, 2025 |
| Example Error Codes | 550 5.7.26 (Sender blocked due to failed authentication) | No specific codes published solely for new bulk sender rules. Typical errors include: 421 TS01 (temporary delays), 554 5.7.9 (policy-related rejections) |
550 5.7.15 Access Denied (and others, depending on the issue) | No publicly specified error codes dedicated to these changes |
| Additional Notes | Encourages use of Google Postmaster Tools for monitoring reputation and diagnostics. Supports BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification) for displaying brand logos in emails after meeting strict DMARC requirements (p=quarantine or p=reject). BIMI is also gaining support among other major mailbox providers as a trust-building standard. | Offers Yahoo Complaint Feedback Loop (FBL), providing data on users marking emails as spam – key to list and reputation management. Also launched the ‘Insights Dashboard’ in Sender Hub for monitoring key metrics and sender reputation. | Introduces its own sender reputation scoring system. Emails are scanned by Microsoft Defender. Plans are in place for a High Volume Email (HVE) service for internal mass sends in Exchange Online. | Emphasizes high content quality and positive user engagement as primary email deliverability factors. Apple Mail Privacy Protection (MPP) may impact accuracy of open rate metrics. |
These changes are not just technical challenges, they’re also a clear signal that mailbox providers are taking the quality of inbox content more seriously than ever. Adaptation is essential and requires a proactive approach, especially in light of the new regulations around email deliverability:
Conduct systematic audits of your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC setup, and verify domain alignment (P2 Header From vs P1/DKIM domain).
Implementing one-click unsubscribe (with a visible link and List-Unsubscribe / List-Unsubscribe-Post headers) is an absolute necessity.
Remember to process unsubscribe requests within the required timeframe.
Track spam complaint rates using FBL data and tools like Google Postmaster Tools.
Pay attention to the SMTP error codes returned by mail servers (like those listed above) – they can reveal issues with email deliverability or technical setup.
This is an ongoing process. Regularly remove inactive addresses, hard bounces, and promptly honor unsubscribe requests.
Check PTR records for your sending IPs and make sure your sender domain (P2 From) has valid MX records.
Ensure your emails comply with RFC 5322, paying particular attention to the correctness of the domain used in the “From” header.
If your messages are likely to be forwarded, implementing ARC headers will help preserve authentication status.
Send content that’s expected and valuable to your audience.
Use a consistent and recognizable sender identity, and consider enabling replies to the sending address.
To help you navigate the new requirements, we’ve prepared a practical checklist of actions you should take to maintain compliance:
At EmailLabs, we understand that adapting to all these requirements can feel overwhelming. That’s why our platform is designed to provide you with the tools and data necessary to maintain high email deliverability and ensure compliance with the latest standards. Here’s how we support you:
In our web app, you’ll find an intuitive “Sender Authorization” configurator that guides you step-by-step through generating SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records for your sending domain.
The DMARC policy, especially stricter settings like p=reject or p=quarantine, is a key element for sender authorization and protecting your brand in email communication.
We give you direct access to the most important data in the EmailLabs web app. You can monitor detailed message logs in real-time, including returned SMTP error codes, and track spam complaint rates thanks to Feedback Loop (FBL) data.
This gives you full visibility into your delivery performance and how receiving servers are handling your messages, which is essential for compliance with the new email deliverability regulations.
While proactive monitoring of your metrics and reputation is your responsibility (using the tools available in the web app), our Technical Support Team is ready to help.
If you notice warning signs, encounter specific issues, or need guidance interpreting the data – reach out to us. We’ll help you find a solution.
We provide the data (e.g., bounces, FBL complaints) necessary for effective contact list management and compliance with new email deliverability regulations.
However, please note: list optimization itself (e.g., segmentation, removing inactive addresses), as well as technical implementation of unsubscribe processes (e.g., updating subscriber status in your database after a click or List-Unsubscribe signal), happens on your side – within your CRM, e-commerce platform, etc.
In the latest version of our web app, we’ve introduced the ability to store and manage contact lists.
This feature is designed for email campaigns sent directly from the EmailLabs web app, making segmentation and sending easier.
Note: it is not currently intended for managing contacts for messages sent via API or Cloud SMTP.
Our mission is to provide you with reliable sending infrastructure and the tools needed to run effective, standards-compliant email communication. We give you control over the critical technical aspects and deliver the data necessary for making informed decisions.
The changes introduced so far represent a significant step forward in the evolution of email marketing standards, but they’re certainly not the end.
We can expect major mailbox providers to continue their efforts toward greater security, transparency, and quality of inbox communication, to stay aligned with future compliance expectations.
A perfect example of this trend is Gmail’s recent update to the ‘Promotions’ tab, which now sorts emails by relevance rather than just date.
This means the algorithm actively promotes emails with higher engagement (opens, clicks) to the top of the inbox, pushing less relevant content further down.
It’s direct proof that technical compliance alone is no longer enough – quality and content alignment are becoming key.
The key to future success will be a proactive approach, investment in best practices, building transparent relationships with your audience, and using tools and services that help ensure compliance and maintain high deliverability.
The world of email marketing is constantly changing, and staying ready to learn and adapt is essential.
Don’t let provider requirement changes hurt your campaigns. Act proactively and make sure your emails are more likely to land where they belong – in your customers’ inboxes.
Do you have questions or need help adjusting your sending practices? Contact the EmailLabs expert team!
We live in a world where your customers switch seamlessly between laptops, smartphones, and tablets. They navigate a complex digital ecosystem – checking emails, using mobile apps, and reacting...
We are delighted to announce that Vercom S.A., the company behind the EmailLabs project, has successfully completed the ISO 22301 certification process. This significant achievement underscores our commitment to...
EmailLabs, as part of the Vercom group, proudly announces its full commitment to aligning its ICT services with the latest cybersecurity standards. In response to dynamically changing regulations, the...
We are pleased to announce that MessageFlow, a product from the Vercom S.A. group, has received the prestigious CSA (Certified Senders Alliance) Certification. This recognition not only underscores the...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
When an email travels from sender to recipient, it passes through several critical components of email infrastructure. At the heart of this journey sits the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)...
Best practices, Marketing E-mails
Customer feedback is the fuel for business growth, but gathering it effectively requires more than just a list of questions. Email surveys remain the most direct channel for understanding...
Best practices, Email Marketing, Pytania i odpowiedzi
Mail merge combines a template document with data to create personalized communications. This technique saves time by automatically generating individualized letters, emails, and labels without manual entry. What Is...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
When an email travels from sender to recipient, it passes through several critical components of email infrastructure. At the heart of this journey sits the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA)...
Best practices, Deliverability, Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Pytania i odpowiedzi
The world of email marketing is constantly evolving, and leading mail service providers – Gmail, Yahoo, Microsoft, and Apple – regularly update their guidelines for senders. In recent years,...
Gmail, Google and Yahoo's Requirements
You might have noticed a new item in your Gmail sidebar recently – the “Manage subscriptions” tab, often flagged with a blue notification dot. While Google announced this feature...
IT & Tech, Pytania i odpowiedzi, Technical
Efficient email communication isn’t just about sending messages — it also involves integrating email functionality into your business systems and applications. Email APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) serve as the...
One of the most important yet often underestimated elements in shaping a company’s brand perception is the transactional email. In e-commerce, the design of such messages must be carefully...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements, Yahoogle
2024 brought fundamental changes to email marketing, introducing new, stringent requirements for senders. Since February 1, 2024, Google and Yahoo have started enforcing new deliverability rules, primarily targeting bulk...
We live in a world where your customers switch seamlessly between laptops, smartphones, and tablets. They navigate a complex digital ecosystem – checking emails, using mobile apps, and reacting...