Email Authentication, Sending Reputation
Email Authentication, Sending Reputation
In the realm of email, sender authorization is a powerful tool wielded by local and global providers like Gmail, Yahoo, and AOL to combat spam. Additionally, as an authenticated sender, you can immediately avoid spam filters, enhancing the likelihood of your campaigns successfully reaching recipients’ email inboxes. Moreover, ISPs will mark your email messages as authenticated, helping to build trust between you and your subscribers and ultimately increasing the possibility of your emails being opened.
In summary, sender authorization is a feature in the EmailLabs panel that allows you to authenticate your sending domains. It protects your account from unauthorized use by third parties and is a significant security measure against spoofing, phishing attempts, and having our messages marked as spam.
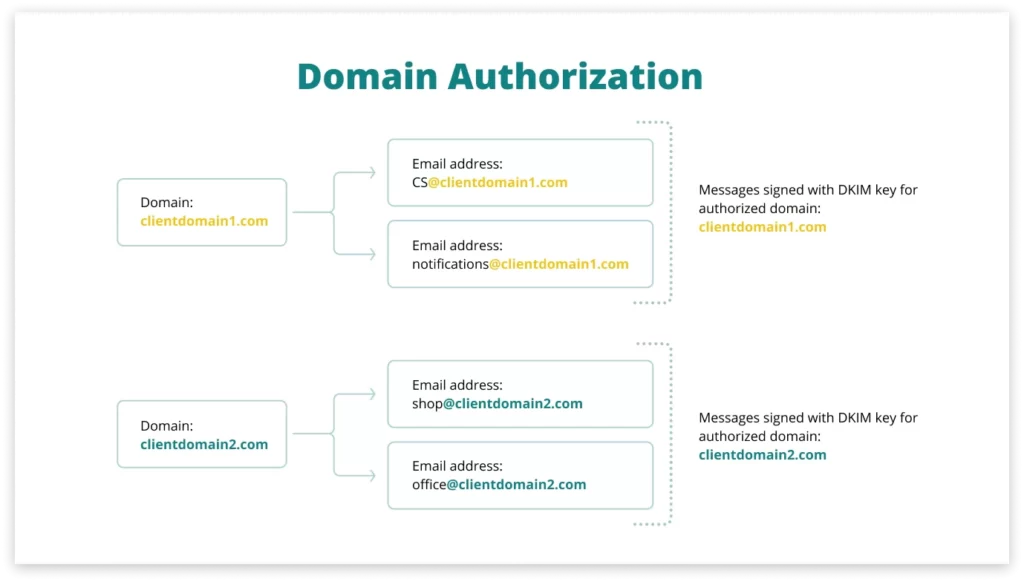
If you have authorized multiple “From” domains in your EmailLabs panel, each of them will sign “its” messages. This means that emails sent from an address associated with a specific domain will be appropriately signed by that domain.
Domain authorization can be configured in the EmailLabs panel in the Admin > Sender Authorization tab.
In the subsequent sections of the article, we will guide you on correctly navigating through the configuration process in our administration panel:
DKIM, which stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail, is an email message authentication protocol that creates a digital signature used by email providers to verify the email sender’s identity. When authorizing a domain, the EmailLabs system generates a unique record that must be added to the DNS settings of a selected domain. It authorizes a domain and enters the DKIM key, which acts as additional authentication for your mailings. This allows the authorized domain to sign your emails with its DKIM key.
In essence, sender authentication in EmailLabs involves generating unique records in the panel and adding them to the domain DNS settings.
DKIM provides a method for validating the identity of the sending domain, which is associated with the message, through cryptography-based authentication methods. The entire process resembles the asymmetric encryption approach of PGP and operates as follows:
Shortcomings in email sender authentication often lead to the classification of our messages by providers like Google or Yahoo as SPAM. Such a situation adversely affects the sender’s reputation and results in a decline in the reputation of the “From” domain and IP address. The consequence is a reduction in e-mail deliverability.
Major Problems That Occur When Sender Authorization is Missing.
To fully understand the importance of proper email sender authentication, it is certainly worth exploring the relationships between deliverability, spam prevention, sender reputation, and security. In the following section, we delve into this topic.
Maximize your email deliverability and security with EmailLabs!
Deliverability and sender reputation, also known as sending reputation, are two halves of the same logical puzzle. The better the reputation influenced by sender authentication, the greater the chances of successful email delivery.
Is this email originating from an authorized domain?
This question covers one of the fundamental issues providers’ algorithms relentlessly solve. Fortunately, if we have appropriately authenticated our sending domain, we are on the way to building the sender’s reputation. What does it mean to have a good reputation? Google defines it nicely:
“High reputation has a good track record of a very low spam rate and complies with Gmail’s sender guidelines. Mail will rarely be marked by the spam filter.“ – Google, support.google.com.
Sender reputation typically involves two dimensions – the reputation of the “From” domain and the reputation of the IP address, encompassing a variety of metrics.
A bad domain or IP address reputation indicates a significant volume of unsolicited communications has been sent from that particular infrastructure. As a result, such emails will most likely be rejected or marked as spam.
Best Practices to Improve and Protect Your Domain Reputation:
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) assess a substantial number of factors associated with an IP address such as: spam rate, hard bounce rate, or the presence of Realtime Blackhole Lists RBL (Realtime Blackhole List) Based on this evaluation, providers reject potentially unwanted emails at the server level or mark them as spam. Based on this evaluation, providers reject potentially unwanted emails at the server level or mark them as spam.
Have you considered what factors can negatively affect your IP reputation?
Mailchecker.net – this powered by EmailLabs tool provides a straightforward way to assess emails directly from your browser, offering guidance on improvements for higher deliverability. Mailchecker.net was designed with marketing emails in mind, but it also effectively verifies transactional messages. The spam test examines the domain and IP address reputation, authentication quality, code correctness, and more. By improving the lowest-rated criteria, you increase the chances of your emails reaching your subscribers’ inboxes.
Google Postmaster Tools enables senders to analyze the performance of their domain in the Gmail service. This tool provide domain and IP reputation insights by analyzing various met. Based on these metrics, Google assigns a reputation score to the domain and IP address used for sending emails. This score helps email senders understand how their emails are being perceived by Gmail’s spam filters and can provide insights into areas for improvement to enhance deliverability.
SNDS (Smart Network Data Services) – analyzes the collected data to assess the reputation of the sending domain and IP addresses. Reputation scoring is based on various factors such as email volume, engagement rates (open and click-through rates), complaint rates, spam trap hits, and adherence to industry best practices and email authentication standards (e.g., SPF, DKIM, DMARC).
5 Ways to Check Sending Reputation
In 2024, sender authentication is even more critical due to new requirements from providers like Google and Yahoo. The aim of these changes is primarily to protect and provide a comfortable experience for the global community of email users.
“No matter who their email provider is, all users deserve the safest, most secure experience possible, … in the interconnected world of email, that takes all of us working together. Yahoo looks forward to working with Google and the rest of the email community to make these common sense, high-impact changes the new industry standard.” ” – Marcel Becker, Sr. Dir. Product at ” Marcel Becker, Sr. Dir. Product at Yahoo. “
One might feel overburdened in this web of rules even though it’s about something other than introducing new elements. ISPs aim to compel senders to adhere to well-established best practices, that have recently evolved into mandatory guidelines.
In 2024 authentication with SPF and DKIM and maintaining SPAM Complaints below the 0.3 threshold are absolute foundations for all senders. Meanwhile, those who send over 5000 messages per day must implement a DMARC at the “p=none” policy.
Overall, if we aim to keep high deliverability, we should promptly implement all required authentications. The deliverability claim for 2024 can surely be “No Auth, No Entry”.
A comprehensive article on Google and Yahoo requirements is here.
Google reported that a 75% reduction in the number of unauthenticated messages received by Gmail users contributed to blocking billions of malicious messages with greater precision. – Google, October 2023. Hence, it is crucial to authenticate the email sender.
As recipients of hundreds of emails daily, we also bear the responsibility not to click on a link that could cause financial losses in our company.
A cybercriminal might exploit our colleague’s compromised email address to carry out a phishing attack. Therefore, in case of doubt, it is worth verifying SPF, DKIM, and DMARC authentications; moreover, each bulk sender should consider implementing BIMI.
Here, we share our Ethical Hackers’ anti-phishing practices – that might prevent you from opening Pandora’s box with your next e-mail.
According to Statista, in 2022, the monetary damage caused by cybercrime in the United States reached a peak of 10.3 billion U.S. dollars. On the other hand, the global average data breach cost was 4.45 million U.S. dollars.
Cybercrimes impact global income, prompting law enforcement efforts to keep pace and elevate security levels worldwide. Below, we share two significant acts you should know about while managing commercial e-mail traffic.
The GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), established in 2018 in Europe.
GDPR focuses on securing European citizens’ private data and determining how businesses handle such information. A must-have for each company that operates within Europe and processes personal data such as email addresses.
The CAN-SPAM ACT, established in 2003 in the USA,
The act was designed to penalize unsolicited commercial electronic mail transmission. It aligns seamlessly with Yahoo’s requirements. This law compels all senders to include an unsubscribe option and prevent emails from being routed through unauthorized servers. Notably, an essential rule prohibits the use of false or misleading headers in the “From,” “To,” and “Reply-To” fields.
Authenticating the domain and IP goes beyond meeting Google and Yahoo requirements; it’s also crucial for compliance with law enforcement in almost every part of the world.
Remeber, in the EmailLabs panel, you can sign a GDPR agreement that defines the terms of processing personal data and both parties’ responsibilities regarding data protection.
Go to the Administrator tab > GDPR.

After introducing the elements behind email sender authentication, let’s proceed to the configuration process using the free EmailLabs configurator as an example.
In the EmailLabs panel, you can generate all the unique records, including DKIM, Tracking, Return Path, and DMARC, which you should apply to your domain/domain’s DNS records.
You must follow similar steps for every new domain “From” to which you intend to send emails. In the case of accessing DNS in your company, you may discover that the assistance of an administrator or the IT department is necessary.
Detailed instructions for configuring the “From” domain in EmailLabs.
If there is concern about adding any entries to DNS settings of your “From” domain, it is advisable to choose a subdomain and implement authentication for only a proportion of email addresses.
Subdomain tracking pertains to monitoring email performance metrics associated with each subdomain, including open rates, click-through rates, bounce rates, and more. This capability enhances in-depth campaign effectiveness analysis and facilitates appropriate action to improve deliverability.
Detailed instructions for configuring the Subdomain tracking
Configuration of your own Return-Path leading to a subdomain in the main domain helps facilitate the DMARC validation process. This is a simple method to improve the deliverability metrics of your messages.
Detailed instructions for configuring the Return Path in EmailLabs:
Detailed instructions for configuring the DMARC record in EmailLabs
Explore the comprehensive documentation provided by EmailLabs, where we address all questions related to the proper configuration of sender authentication and associated authentications:
Sender Authorization in EmailLabs Panel
If you have any doubts about how to fill in the fields in the EmailLabs panel correctly, please contact our Customer Support at [email protected]
Good Luck!
Gmail has announced significant changes in the requirements for email senders to maintain a good reputation and proper classification of messages in user inboxes starting from February 1, 2024....
Vercom S.A. public joint-stock company to which the EmailLabs project belongs, has been assessed and certified to be compliant with the ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27018 standards. The Vercoms’...
The increasing number of phishing attacks each year, and the projection that this trend will continue to escalate, aren’t likely to astonish anyone. This can be attributed, in part,...
Out of all the things that can go wrong when sending out marketing emails, having your emails end up in the recipient’s spam folder is arguably the most dreaded...
Email Authentication, Security
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that is designed to give domain owners the ability to protect their domain from unauthorized use, commonly known as email spoofing. Spoofing occurs...
With the emergence of the Covid-19 pandemic, many brands have been challenged to adapt in a short period to the changed reality and new consumer attitudes. That meant reorganizing...
Have you ever sent an email in haste and immediately wished you hadn’t? It happens more often than we’d like to admit. If you ever find yourself in this...
One safe and easy way to keep track of your digital interactions is to save emails as PDFs. However, do you know the best ways to easily turn your emails into PDF files? In this article, we’ll look into the different ways you can do to turn your emails into accessible PDF files. Let’s start! Key Takeaways To save emails...
Sending large files online can sometimes feel like maneuvering through a maze with unexpected twists and turns. The frustration of hitting attachment size limits or dealing with slow uploads...
Have you ever sent an email in haste and immediately wished you hadn’t? It happens more often than we’d like to admit. If you ever find yourself in this...
One safe and easy way to keep track of your digital interactions is to save emails as PDFs. However, do you know the best ways to easily turn your emails into PDF files? In this article, we’ll look into the different ways you can do to turn your emails into accessible PDF files. Let’s start! Key Takeaways To save emails...
Sending large files online can sometimes feel like maneuvering through a maze with unexpected twists and turns. The frustration of hitting attachment size limits or dealing with slow uploads...
Are you a bit baffled by email protocols like IMAP, POP3, and SMTP? Have no fear – this article is here to explain it all. If you have ever...
In 2024, global providers like Gmail and Yahoo have implemented a series of changes, primarily targeting bulk senders. These changes, already in effect, are part of a continuous update...
In the face of dynamic technological advancements and increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, ensuring network security has become crucial. Dozen security incidents present a challenge that we cannot afford to...
Google and Yahoo's Requirements
2024 marks a turning point in the fast-paced world of email deliverability, as this is the year when Google and Yahoo updated their sender requirements. With the enforcement period...
Best practices, Email Marketing
B2B email marketing – it’s a term you’ve likely heard before, but what does it really entail? And, more importantly, how can it be done effectively? In this article,...
Deliverability, Sending Reputation
Email sender reputation is one of the most important factors that can determine whether your emails reach the intended recipient or not. So, what is the email sender reputation,...